TLS (Transport Layer Security)
Secure Communication between applications
Properties
- Authenticated
- Integrity Protected
- Confidential
- Secure against replay and deletion
Building Blocks
- Strong block ciphers (AES, Twofish, ...)
- Authenticated encryption mpdes (GCM, CCM)
- Diffie-Hellman Key agreement
- Groups that yield small keys and fast DH operations (ECC)
- Public key authentication with certificates
- Authentication trough signatures
- Cryptographic hash functions for key generation (HKDF) (e.g. AES session keys)
A cipher suite determinces the set of cryptographic algrogithms to be used.
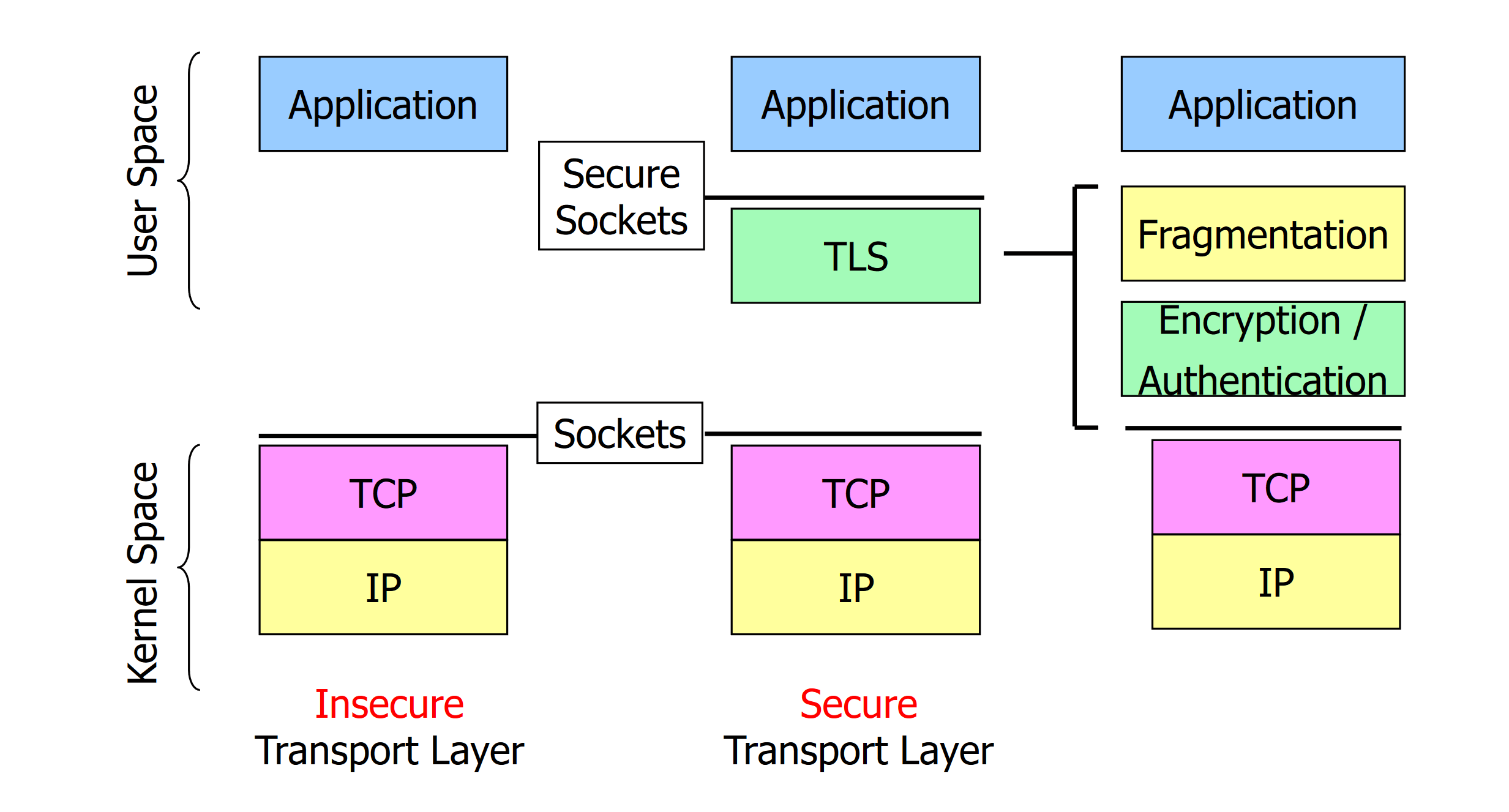
Layer
- TLS works on top of TCP
- Can be implemented in user space (directly in the application software)
- Does not have to worry about lost/retransmitted data
Protocol stack
TLS 1.3 Record Protocol
TLS Record Protocol
Defines the TLS packet format; all data that are using TLS are transported within TLS Records
Handshake Protocol
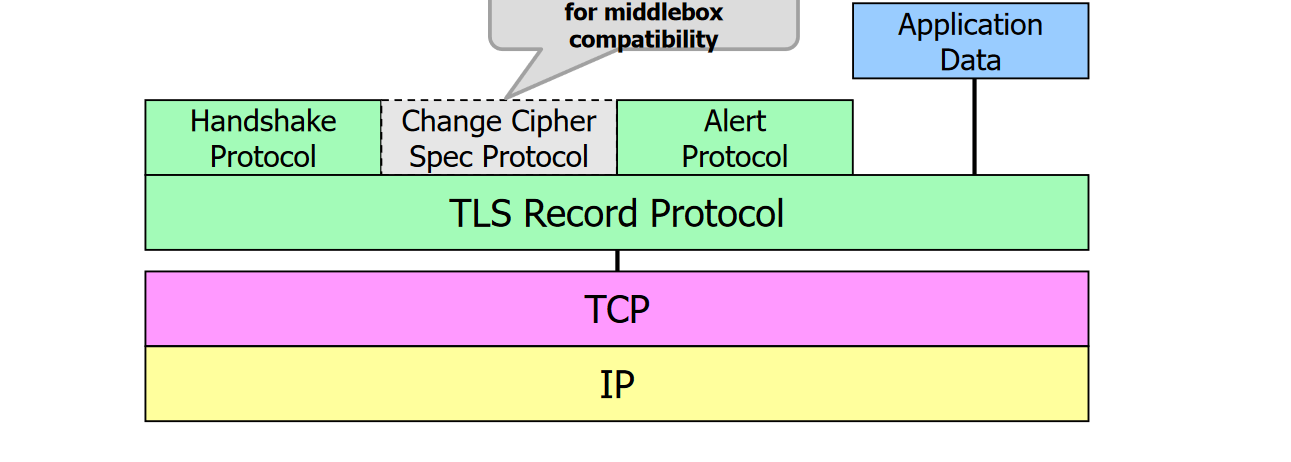
Used to establish TLS sessions
Change Cipher Spec Protocol (deprecated)
Dummy messages only. In TLS 1.2, it indicated switching to the newly negotiated secure communication relationship and keys
Alert Protocol
Indicates warnings/errors (e.g., certificate expired)
Application Data
Data meaningful to applications (not for TLS)
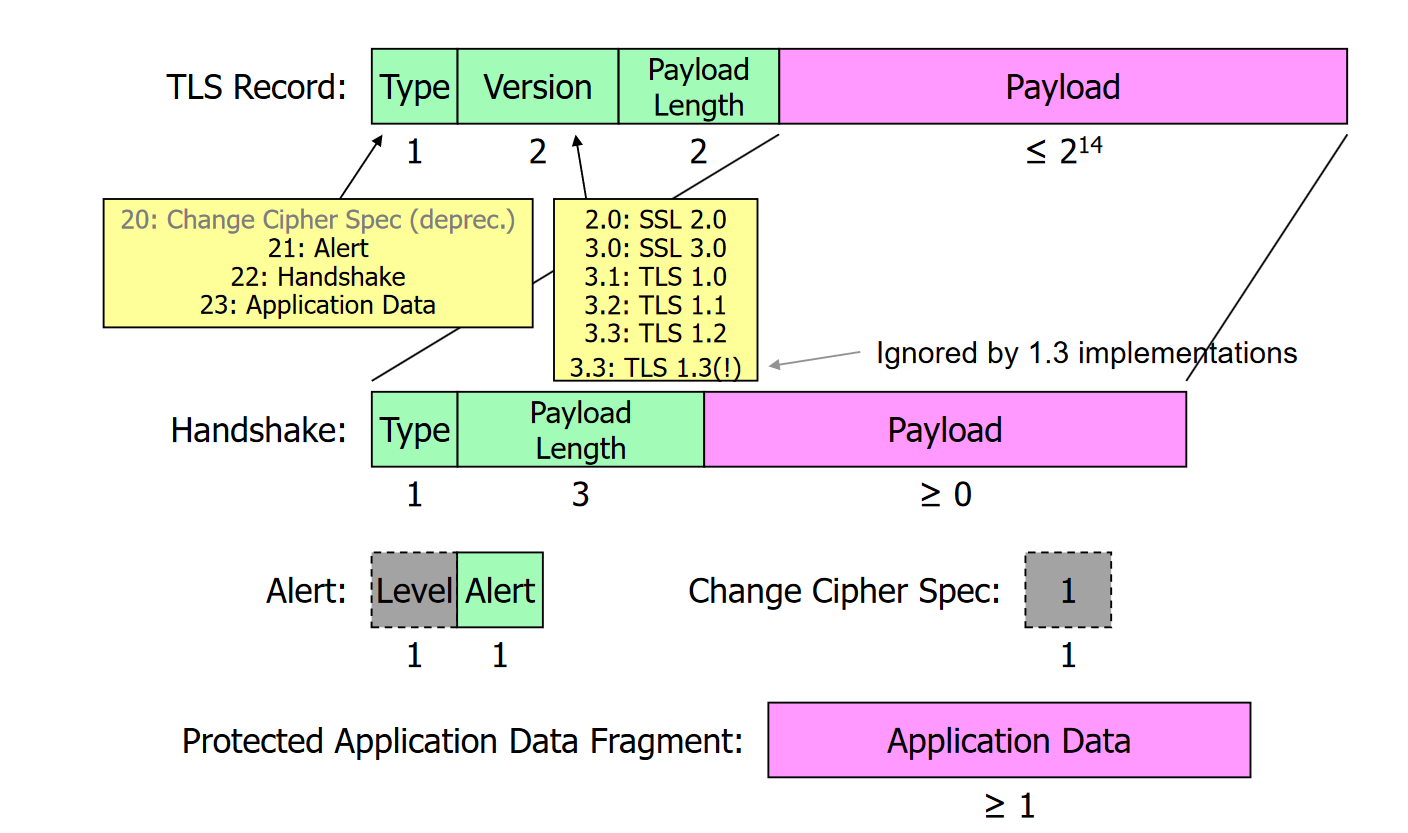
TLS message formats
Phases
Handshake
Authentication and establishment of cryptographic algorithms and key material
Data Exchange
Exchange protected data
Connection teardown
Disconnect safely