GPIO
A GPIO may have multiple functions. The active function can be selected using the GPFSEL register.
Base Address>: 0x7e20'0000
Can be found in the PDF on section 5.2 (Register View)
Register
| Register | Anwendung | Bits |
|---|---|---|
| GPFSEL | Function selection for GPIO | 3 |
| GPSET | Set Value for GPIO | 1 |
| GPCLR | Clear Value for GPIO (Set to 0x00) | 1 |
| GPLEV | Read Pin Level | 1 |
Access
Kommandozeilen Befehl um die GPIOChip Nummern für Zugriff über pseudo Filesystem
ls gpiochip*/device/driver
Pseudo Filesystem
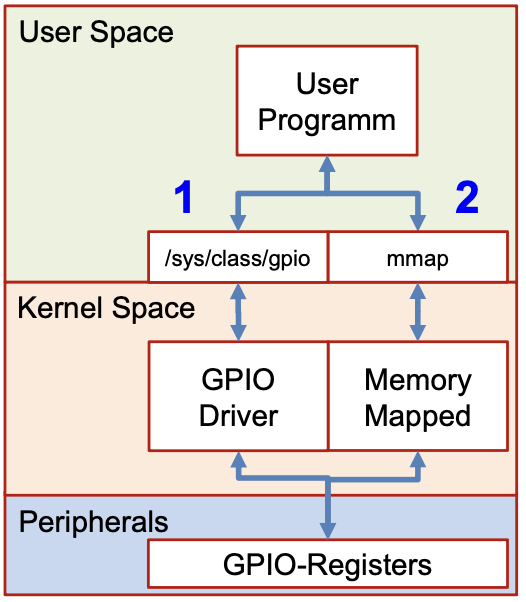
GPIO can be accessed using the pseudo file system mapped at "/sys/class/gpio"
- Requires driver for GPIO
- Portable to other HW, works everywere
- Less hassle with addressses
Enable GPIO
echo <gpio-pin> > /sys/class/gpio/export
Set Direction of GPIO
| Direction | Value to Write |
|---|---|
| Read pin | in |
| set pin | out |
XX => GPIO-PIN-Number
echo "direction" >> /sys/class/gpio/gpioXX/direction
Value of GPIO
| State | Value to Write |
|---|---|
| HIGH | 1 |
| LOW | 0 |
Set Value
echo "1" >> /sys/class/gpio/gpioXX/value
Read Value
cat /sys/class/gpio/gpioXX/value
C-Code
Export GPIO
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("/sys/class/gpio/export", "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("Error opening file in gpio_init %s\n", str);
return 1;
}
fprintf(fp, "%i", gpio);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
Set Value
void fs_gpio_set (int gpio, int val)
{
FILE *fp;
char str[100];
sprintf(str, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%i/value", gpio);
fp = fopen(str, "w");
if (fp== NULL) {
printf("Error opening file in gpio_set %s\n", str);
return -1;
}
fprintf(fp, "%i", val);
fflush(fp);
fclose(fp);
}
Read Value
int fs_gpio_get (int gpio)
{
FILE *fp;
char str[100];
int ret;
sprintf(str, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%i/value", gpio);
fp = fopen(str, "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("Error opening file in gpio_read %s\n", str);
return -1;
}
fread(str, 101, 1, fp);
sscanf(str, "%i", &ret);
fclose(fp);
return ret;
}
Memory Mapped
When using Memory Mapped / DMA (Direct Memory Access), the gpio location must be translated to the memory address.
The Physical Address is 35bit!
void *virtual_gpio_base; //define global pointer
int mmap_virtual_base()
{
int m_mfd;
if ((m_mfd = open("/dev/mem", O_RDWR)) < 0)
{
printf("FAIL by open /dev/mem\n");
return m_mfd;
}
virtual_gpio_base = (void*) mmap(NULL, sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE),
PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, m_mfd, GPIO_BASE_ADDR);
close(m_mfd);
if (virtual_gpio_base == MAP_FAILED) {
return errno;
}
return 0;
}
Setting and clearing of single gpio pins
#define GPIO_SET0 (0x0000001c) // GPIOSET0 offset
#define GPIO_CLR0 (0x00000028) // GPIOCLR0 offset
void *virtual_gpio_base; //define global pointer
static void mmap_gpio_set(int gpio, int value)
{
uint32_t *gpio_reg;
if (value == 1){
gpio_reg = (uint32_t *) (virtual_gpio_base + GPIO_SET0);
}
else {
gpio_reg = (uint32_t *) (virtual_gpio_base + GPIO_CLR0);
}
*gpio_reg = (0x1 << gpio);
}
I2C
Read / Write Cycle
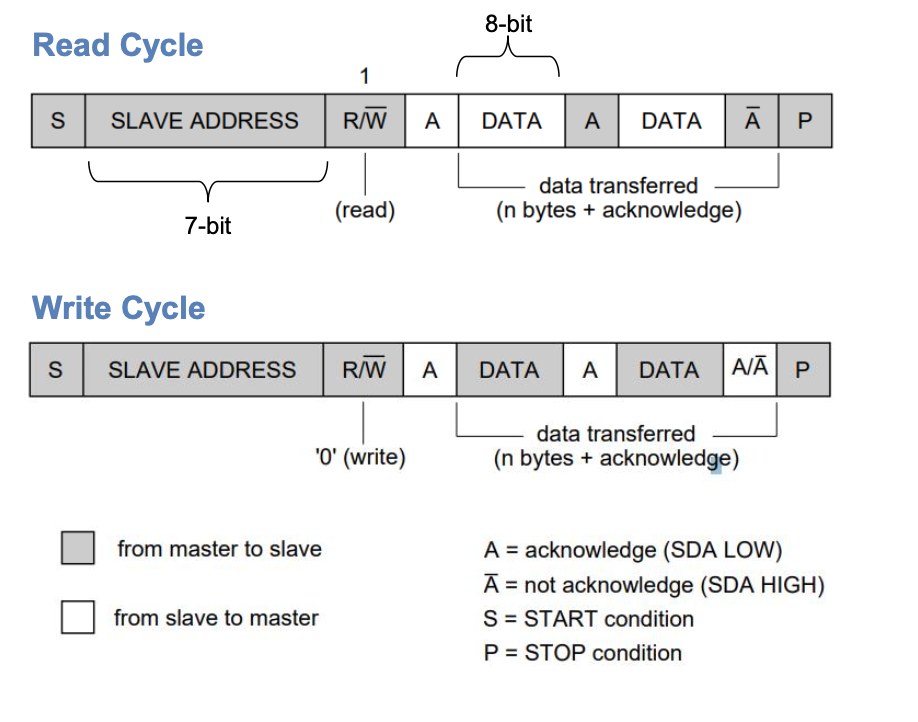
Writing / Reading Data
-
For more details checkout CT2 I2C
-
Only one driver can open the bus
#include <linux/i2c-dev.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int fd;
char *filename = "/dev/i2c-1";
if ((fd = open(filename, O_RDWR)) < 0) {
/* ERROR HANDLING: you can check errno to see what went wrong */
perror("Failed to open the i2c bus");
exit(1);
}
// Sets up the I2C controller with I2C-bus mode and I2C slave address
int addr = 0x20;
if ( ioctl(fd, I2C_SLAVE, addr ) < 0) {
printf("Failed to acquire I2C bus access and/or talk to slave.\n");
exit(1);
}
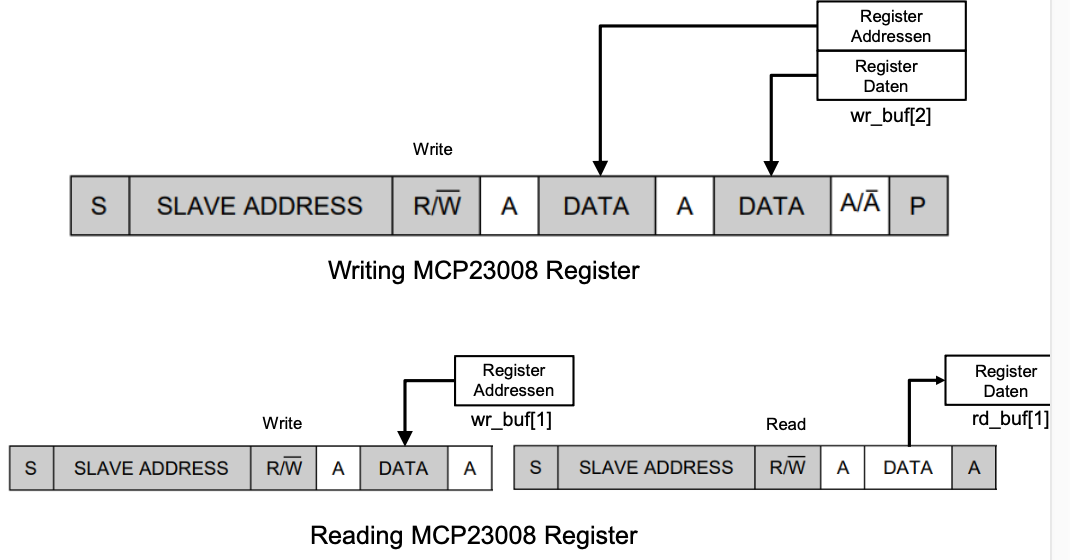
// WRITE
uint8_t wr_buf[2];
wr_buf[0] = register_address;
wr_buf[1] = register_data;
if ( write(fd, wr_buf, 2) != 2 ) {
printf("Failed to write to the i2c bus.\n");
}
//READ
uint8_t data = 0;
uint8_t wr_buf[1];
uint8_t rd_buf[1];
wr_buf[0] = register_addr;
if ( write(fd, wr_buf, 1) != 1 ) {
printf("Failed to write to the i2c bus.\n");
}
if ( read(fd, rd_buf, 1) != 1 ) {
printf("Failed to read from the i2c bus.\n");
} else {
data = rd_buf[0];
}