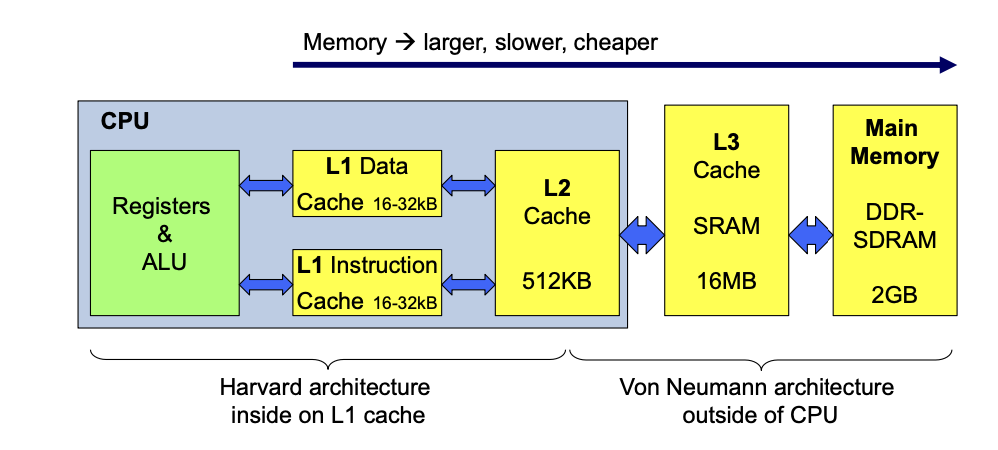
Cache
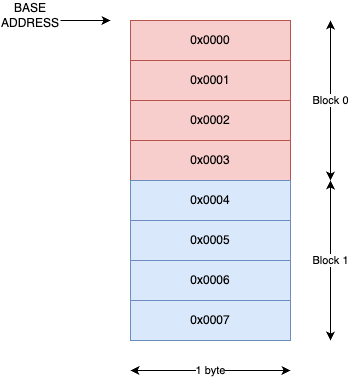
- Blocks sind in diesem Beispiel 4 Byte lang, können aber auch grösser, bzwh. kleiner sein.
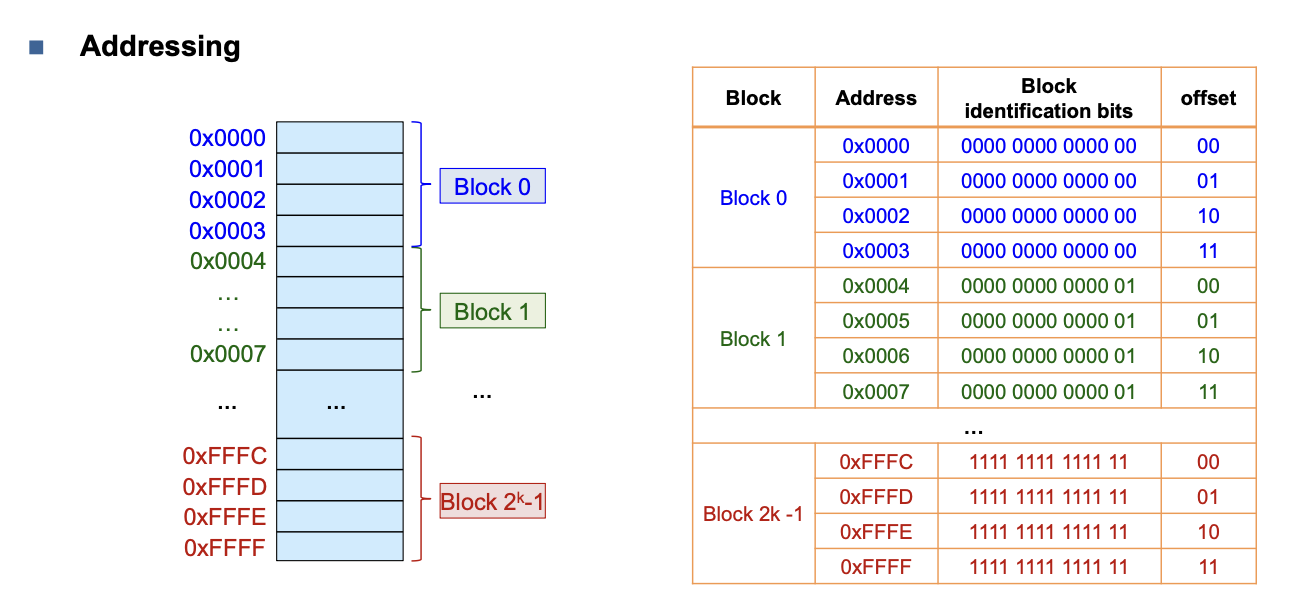
Aufbau im Memory

- Gruppen von Blocks werden im Memory hintereinander gebilted.
- Die CPU kopiert gewisse Blocks mit deren ID in den Cache.
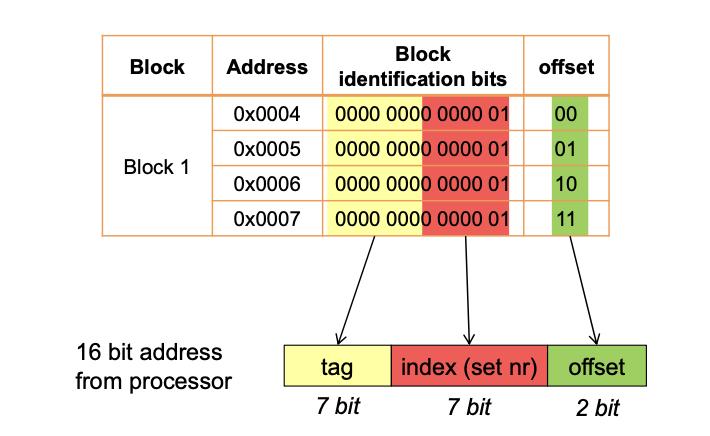
| Bezeichnung | Symbol |
|---|---|
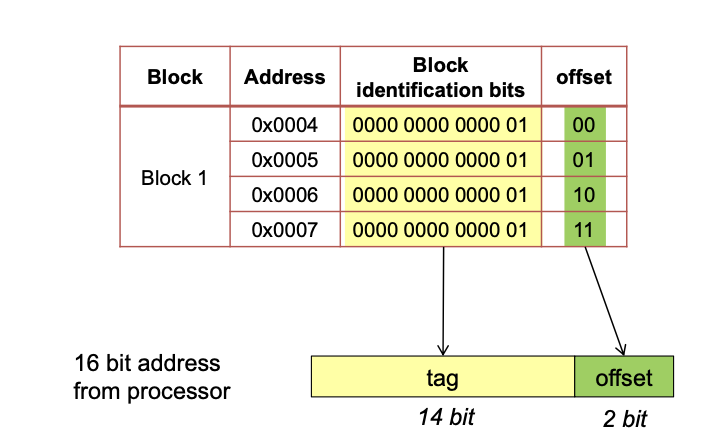
| Anzahl Bits für die Adressierung | t + i + o |
| Anzahl Bits für Offset | o |
| Anzahl Bits für Index | i |
| Anzahl Bits für Tag | t |
- Grösse des RAM in Bytes (Memory Size): 2^(t+i+o)
- Anzahl Zeilen im Cache: 2^i
- Grösse einer Cache-Zeile in Bytes (nur Nutzdaten): 2^o
- Grösse des Cache in Bytes (Cache Size, nur Nutzdaten): 2^i * 2^o
Cache Organization
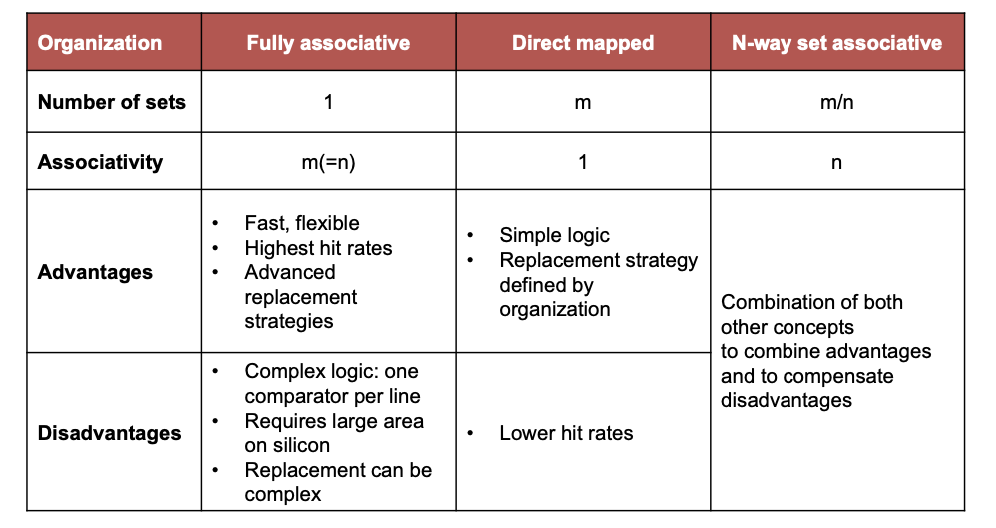
Fully Associative
Direct Mapped
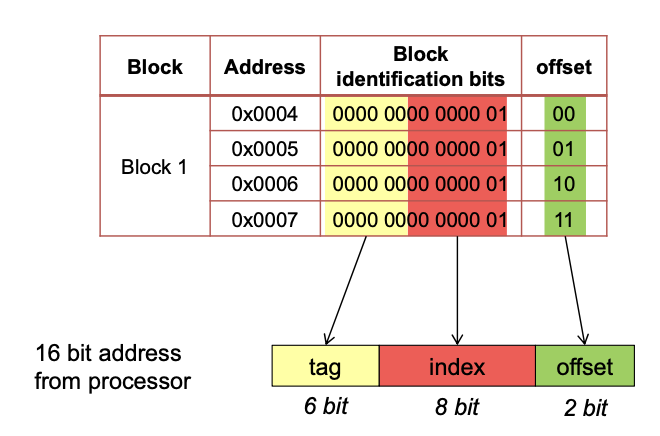
N-Way Set Associative
- max index corresponds to number of sets (s=m/n)
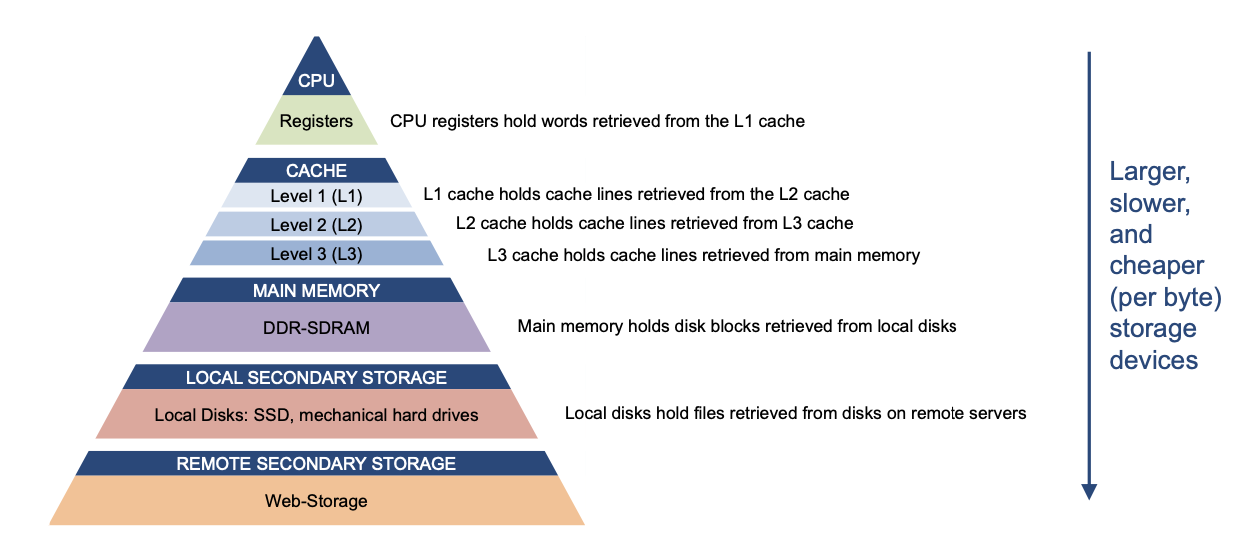
Memory Hierarchy
 ]
]
Principle of locality
for (i=0; i < 10000; i++) {
a[i] = b[i]; // spatial locality
}
if (a[1234] == a[4320]) { // temporal locality
a[1234] = 0;
}